skysil filtration media
European Parliament recognises access to drinking water as a fundamental human right
Chalcedonite is a mineral of organic origin, mined in the open-pit mine in Inowłódz. Due to its origin (skeletons of organisms living in shallow seas in the Jurassic era), chalcedonite contains silica with a highly developed pore system.
Chalcedonite, after appropriate treatment, becomes a basis for the production of effective filtration materials, and its physical properties (high porosity) and chemical composition (SiO2>97%) predispose it to be used in drinking water treatment technology.
A number of technological challenges are encountered in water treatment processes that sometimes cause sleepless nights for designers, contractors and operators of Water Treatment Plants.
Each of the bed variants has distinctive properties, which translate into a superior effectiveness in a given application.
Application of SkySil chalcedonite filter media
- They provide security for designers as the high efficiency of the filtration media allows a wider range of applications.
- They guarantee peace of mind for the water treatment plant operator (changes in raw water parameters, which we have to deal with repeatedly during the long-term operation of the well, are imperceptible to the end user), as the high-efficiency reservoirs adapt to the operating conditions.
- The availability of filtration media will not hinder contractors from completing the project on time.
| SkySil Fe Ammonio | SkySil Fe | SkySil Mn | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing Fe | |||
| Reducing Mn | |||
| Reducing NH4+ | |||
| Suspended solids filtration | |||
| Increasing water plant capacity | |||
| Improving work safety and stability | |||
| Reduction of flushing water flow | |||
| Intended use | Water treatment plants | Water treatment plants | Domestic water treatment plants |
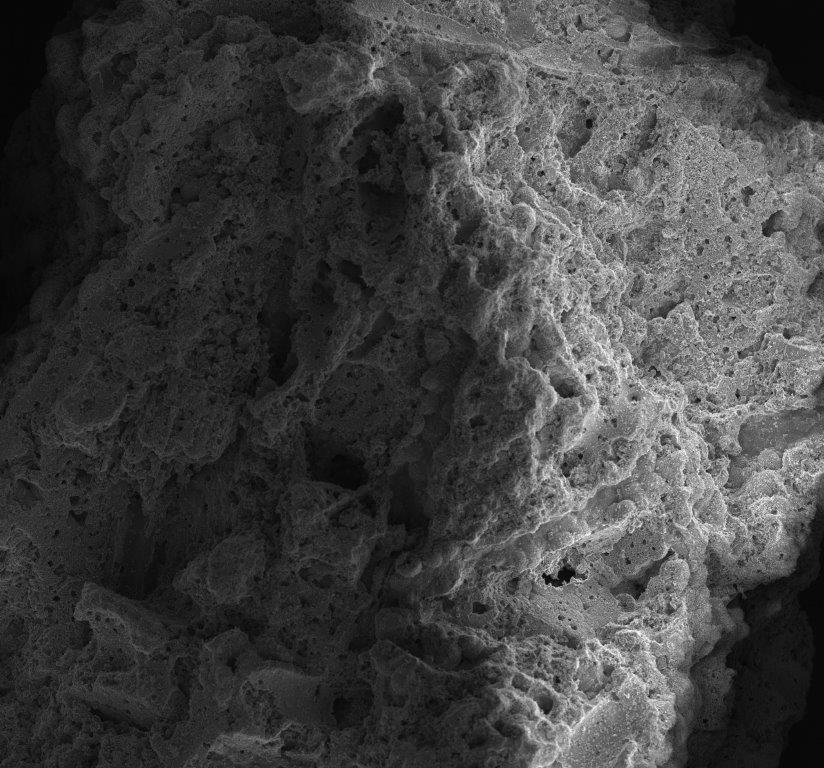
The most important characteristic of chalcedonite is its porosity, which can reach up to 30%. Due to this quality, beneficial micro-organisms can grow in the filtration media and play a key role in removing contaminants such as manganese and ammonium ion from the water. Numerous studies confirm that the process of manganese reduction begins right in the pores of the filter media.
Alongside the high porosity, there are other technological advantages associated with the use of chalcedonite, such as efficiency in the removal of mechanical impurities, extension of filtration cycles or the possibility of using higher filtration rates. All these unique physicochemical properties are the source of numerous advantages over quartz sand.
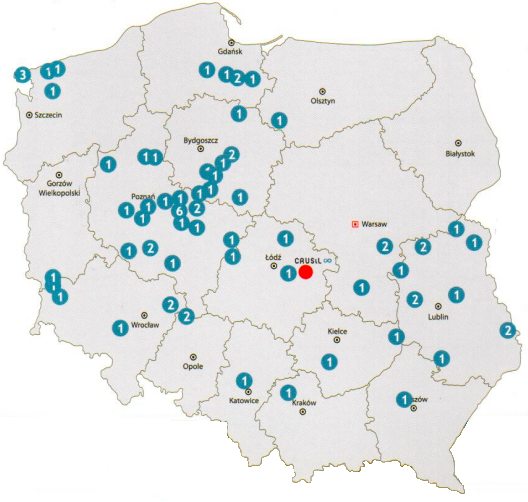
The use of the SkySil chalcedonite filter media in many waterworks in Poland has yielded positive results, especially in smaller rural facilities that often face technological problems.
| PARAMETER | SkySil | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SkySil Fe Ammonio | SkySil Fe | SkySil Mn | ||
| Iron removal potential | ≤ 20 | ≤ 20 | ≤ 15 | mg Fe/dm3 |
| Manganese removal potential | ≤ 1,5* | ≤ 1,5* | ≤ 5,0 | mg Mn/dm3 |
| Ammonium ion removal potential | ≤ 2,0* | ≤ 2,0** | ≤ 2,0** | mg NH4+/dm3 |
* after prior natural development
t = 20÷40 days
** after prior natural development
t + 50%
Key benefits of the SkySil filter media:
- Lower de-gelatinisation zone – up to 30% compared to quartz sand.
- High iron removal efficiency – (up to 98%).
- High mass capacity – extending filtration cycles and reducing flushing costs by up to 30%.
- High filtration velocities – up to 20 m/h.
- Favourable hydraulic characteristics – low filter media resistance allows to reduce system operating pressure.
- High porosity – ideal conditions for colonisation of manganese and nitrifying bacteria.
… which saves a significant portion of the funds allocated for the construction or modernisation of water treatment plants, as well as the world’s most precious raw material – water.
As part of our free technology consultation, we provide:
- a proposal for the selection of the SkySil filtration grit (type of material, grain size, backfill height);
- technological indications for the operation and rinsing of chalcedonite bed filters;
- answering technical questions on the use of Skysil deposits in relation to existing solutions;
- case studies
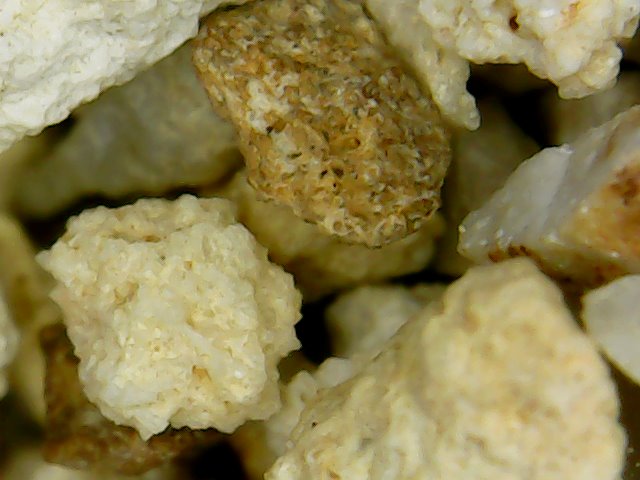

SkySil Fe Ammonio
The SkySil Fe Ammonio filtration media is natural chalcedonite, which has been used in water treatment technology for many years. Due to its developed pore system, the filtration media provides an excellent substrate for the formation of a biological membrane that metabolises ammonium ion. The development of the biofilm inside the pores prevents it from being completely destroyed during the washing process.
An important characteristic of the SkySil Fe Ammonio filtration media is its high mass capacity enabling simultaneous removal of iron and other suspended solids.
Under suitable filtration conditions, the filtration media in the lower layers of the filter acquires the ability to reduce manganese.
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granulation | 0,8 – 2,0 | mm |
| Bulk density | 0,85 – 0,95 | kg/dm3 |
| Specific density | 2,62 – 2,67 | kg/dm3 |
| Grain porosity | ≤ 30 | % |
| Specific surface area | 4,5 - 6 | m2/g |
| Homogeneity coefficient | ≤ 1,5 | - |
| Ingridient | content [%] |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 97,7 – 98,9 |
| Al2O3, MgO, CaO, Fe2O3, K2O | < 2,0 |
| Organic components | < 0,05 |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration rate | ≤ 15 | m/h |
| Iron removal potential | ≤ 20 | mg Fe/dm3 |
| Manganese removal potential | ≤ 1,5* | mg Mn/dm3 |
| Ammonium ion removal potential | ≤ 2,0* | mg NH4+/dm3 |
| Water pH range | 6,5 – 9,5 | - |
| Space above the filter media | 40 | % |
| Air rinse speed | 13 – 17 | L/s·m2 |
| Water rinse speed | 12 – 15 | L/s·m2 |
| Filter media expansion | 25 | % |
* after prior natural development
SkySil Fe Ammonio is characterised by the following properties, which distinguish it from the filtration media present on the market:
- high mass capacity for contaminants, allowing longer filter cycles;
- the high porosity of the grains, accelerating the biological activation of the bed to remove ammonium ion, as well as shortening the time for manganese removal compared to commonly used filter materials;
- low bulk density allowing the load on the filter floor to be reduced, which is particularly important in pressure filters;
- favourable hydraulic characteristics (low bed resistance, including after suspension filtration, allowing a reduction in system operating pressure);
- high filtration rates of up to 15 m/h.
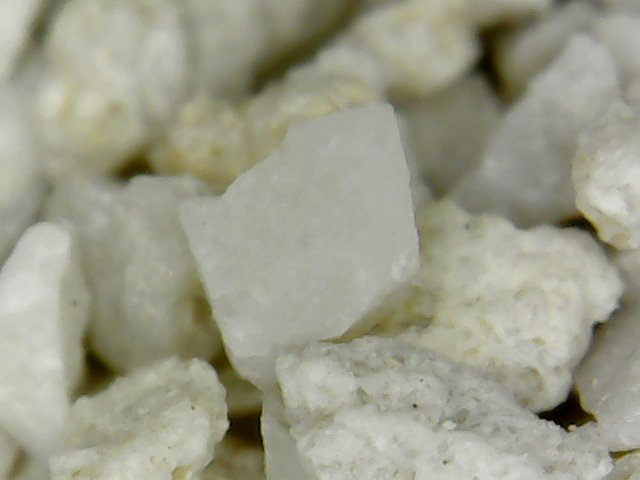

SkySil Fe
SkySil Fe is a lightweight porous cryptocrystalline silica media with increased mass capacity for suspended solids, which is produced by processing natural chalcedonite.
The unique pore structure allows for impressive iron reduction and suspended solids filtration results.
Due to its low bulk density, the SkySil media allows significant savings in rinse water, optimising water treatment processes.
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granulation |
0,6 – 1,2 1,1 – 2,0 |
mm |
| Bulk density | 0,9 – 1,1 | kg/dm3 |
| Specific density | 2,62 – 2,65 | kg/dm3 |
| Grain porosity | ≤ 20 | % |
| Specific surface area | 4,5 – 5,0 | m2/g |
| Homogeneity coefficient | ≤ 1,5 | - |
| Ingridient | Content [%] |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 97,7 – 98,9 |
| Al2O3, MgO, CaO, Fe2O3, K2O | < 2,0 |
| Organic components | < 0,05 |
| Parameter | 0,6 - 1,2 | 1,1 - 2,0 | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filtration rate | ≤ 15 | m/h | |
| Iron removal potential | ≤ 20 | mg Fe/dm3 | |
| Manganese removal potential | ≤ 1,5* | mg Mn/dm3 | |
| Ammonium ion removal potential | ≤ 2,0* | mg NH4+/dm3 | |
| Space above the filter media | 40 | % | |
| Air rinse speed | 8,5 – 13 | 11 – 17 | L/s·m2 |
| Water rinse speed | 7,5 – 12 | 10 – 15 | L/s·m2 |
| Filter media expansion | 25 | % | |
* after prior natural development
The chalcedonite filter media SkySil Fe is characterised by the following properties, which distinguish it from current deposits on the market:
- high mass capacity for contaminants, allowing longer filter cycles - including improved iron removal efficiency;
- low bulk density to reduce the load on the filter floor, which is particularly important in pressure filters;
- favourable hydraulic characteristics (low media resistance, including after filtration of suspended solids, allowing a reduction in system operating pressure).
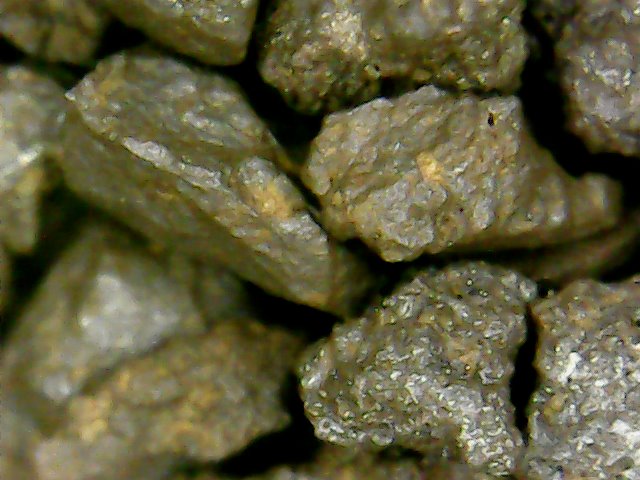

SkySil Mn
SkySil Mn is a high-performance filter media for manganese removal that combines the natural porosity and grain shape of chalcedonite with manganese oxide in the form of Birnessite. The structure and structure of Birnessite means that it readily enters into redox reactions and exhibits a high adsorptive capacity towards manganese providing suitable conditions for further autocatalytic oxidation.
The production process developed at Crusil enables the chalcedonite aggregate to be thoroughly coated with a layer of manganese, so that an immediate manganese reduction effect can be achieved immediately after start-up.
The low bulk density of the SkySil Mn bed (1.0 – 1.1 Mg/m3) enables a proper washing process even at limited pressure and eliminates the risk of clumping and dead zones.
| Parameter | value | unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granulation | 0,6 – 1,2 | mm |
| Bulk density | 1,0 – 1,1 | kg/dm3 |
| Specific density | 2,7 – 2,8 | kg/dm3 |
| Grain porosity | ≤ 15 | % |
| Specific surface area | 3,0 – 3,5 | m2/g |
| Homogeneity coefficienti | ≤ 1,6 | - |
| Ingridient | Content [%] |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 91,4 – 97,7 |
| Al2O3, MgO, CaO, Fe2O3, K2O | < 6,0 |
| Manganese oxides coating the grains | 2,1 – 3,4 |
| Organic components | < 0,05 |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration rate | ≤ 15 | m/h |
| Iron removal potential | ≤ 15 | mg Fe/dm3 |
| Manganese removal potential | ≤ 5,0 | mg Mn/dm3 |
| Ammonium ion removal potential | ≤ 2,0* | mg NH4+/dm3 |
| Water pH range | 6,5 – 9,5 | - |
| Space above the filter media | 40 | % |
| Air rinse speed | 13 – 17 | L/s·m2 |
| Water rinse speed | 12 – 15 | L/s·m2 |
| Filter media expansion | 25 | % |
* after prior natural development
The chalcedonite filter media SkySil Mn is characterised by the following properties, which distinguish it from current deposits on the market:
- high mass capacity for contaminants, allowing longer filter cycles - including improved iron removal efficiency;
- low bulk density to reduce the load on the filter floor, which is particularly important in pressure filters;
- a synthetic coating of manganese oxides on the surface of the bed grains allows for efficient manganese removal right from the start of filter operation. The target operation is carried out in a way that does not require the operator to take any special measures or wait long periods before the manganese precipitation starts;
- favourable hydraulic characteristics allowing a reduction in system operating pressure.